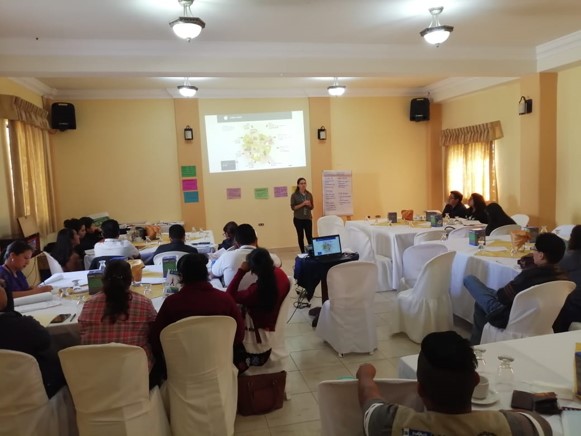
Implementing a multicomponent intervention to improve hypertension control in Central America: a cluster randomized trial in Guatemala
|
Participating institutions name and acronyms |
·
INCAP Research Center for the Prevention of Chronic
Diseases ·
School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine,
Tulane University ·
Institute for Clinical Effectiveness and Health
Policy (IECS) ·
Center of Excellence for Cardiovascular Health
(CESCAS) ·
Department of Family Medicine, University of
Colorado · Ministry of Public Health and Social Assistance of Guatemala |
|
CIIPEC Researchers |
·
Manuel
Ramírez-Zea ·
Diego
Hernández-Galdamez ·
Ana
Lucía Peralta ·
Kristyne
Mansilla ·
Dina
Roche
|
|
Abstract |
The first phase of this project assessed the needs, barriers, and
knowledge gaps of the hypertension control program in the national health
care system of Guatemala.
The second phase of this project, a cluster randomized trial will test
the effect of a multi-level and multi-component intervention program within
the primary healthcare system in Guatemala, on blood pressure (BP) control
among hypertensive patients; will evaluate the adaptability, feasibility,
fidelity, and sustainability of implementing the program in the primary
health care system of Guatemala; and the cost effectiveness of such program
in Guatemala in comparison to usual care. The comprehensive intervention,
which includes protocol-based treatment using a standard BP management
algorithm, team-based collaborative care, BP audit and Feedback, home BP
monitoring, and health coaching on anti-hypertensive medication adherence and
lifestyle modification, will last for 18 months.
This implementation research study presents high public health impact
because it will generate urgently needed data on effective, practical, and
sustainable intervention strategies aimed at reducing BP related disease
burden in Central America and other low-and middle-income countries.
|
|
General objective |
To test whether a multilevel and multicomponent intervention program,
integrated to the primary healthcare system in rural Guatemala, will improve
hypertension control and lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure among
patients with uncontrolled hypertension over an 18-month period compared to
usual care.
|
|
Methodology |
A cluster randomized trial including 36 rural health districts managed
by the Ministry of Health (MOH) of Guatemala. Eighteen health districts will
be assigned to a multicomponent intervention and 18 to usual care. Each health
district will recruit 44 patients aged ≥40 years with uncontrolled
hypertension.
|
|
Project duration |
2017-2022
|
|
Publications related |
Paniagua-Avila, A., Fort, M.P., Glasgow, R.E. et
al. Evaluating a multicomponent
program to improve hypertension control in Guatemala: study protocol for an
effectiveness-implementation cluster randomized trial. Trials 21, 509
(2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-020-04345-8 Fort MP, Paniagua-Avila A, Beratarrechea A, et al. Stakeholder Engagement in the Translation of a
Hypertension Control Program to Guatemala's Public Primary Health Care
System: Lessons Learned, Challenges, and Opportunities. Glob Heart.
2019;14(2):155-163. doi:10.1016/j.gheart.2019.05.005 Aifah A, Iwelunmor J, Akwanalo C,
et al. The Kathmandu Declaration on Global CVD/Hypertension Research and
Implementation Science: A Framework to Advance Implementation Research for
Cardiovascular and Other Noncommunicable Diseases in Low- and Middle-Income
Countries. Glob Heart. 2019;14(2):103-107.
doi:10.1016/j.gheart.2019.05.006 |